Dictionary Meaning -
Homoeopathic Treatment :-
by Oscar E. BOERICKE, M.D.) Are As Below-
For Detail Study Of Above Mentioned Individual Remedy From HOMŒOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICA by William BOERICKE, M.D.:-
(according to Dorland's pocket medical Dictionary)
Any Disorder Characterized By Excessive Urine Excretion. When Used Alone, The Term Refers To Diabetes Mellitus.
Adult Onset Diabetes Mellitus - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Brittle Diabetes - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Characterized By Wide, Unpredictable Fluctuations Of Blood Glucose Values & Difficult To Control.
Bronze Diabetes , Bronzed Diabetes - Hemochromatosis.
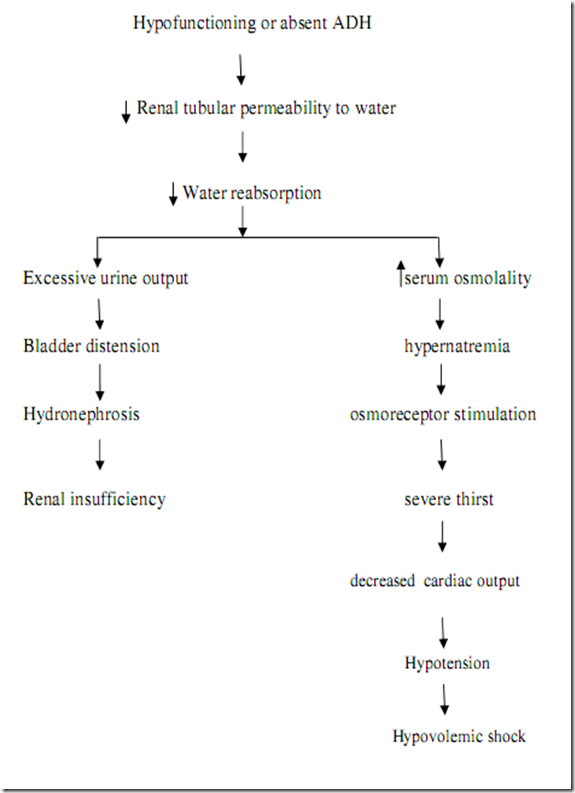
Central Diabetes Insipidus - Diabetes Insipidus Due To Injury Of The Neurohypophyseal System, With A Deficient Quantity Of Anti-Diuretic Hormone Being Released Or Produced, Causing Failure Of Renal Tubular Re-Absorption Of Water.
Gestational Diabetes, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus - That With Onset Or First Recognition During Pregnancy.
Growth Onset Diabetes Mellitus - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Diabetes Insipidus - Any Of Several Types Of Polyuria In Which The Volume Of Urine Exceeds 3 Liters Per Day, Causing Dehydration And Great Thirst, As Well As Sometimes Emaciation And Great Hunger.
Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus ( IDD, IDDM ) - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Juvenile Diabetes Mellitus , Juvenile Onset Diabetes Mellitus - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Ketosis-Prone Diabetes Mellitus - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Maturity Onset Diabetes Mellitus - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Diabetes Mellitus ( DM ) - A Chronic Syndrome Of Impaired Carbohydrate, Protein, And Fat Metabolism Owing To Insufficient Secretion Of Insulin Or To Target Tissue Insulin Resistance. It Occurs In Two Major Forms: Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus & Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Which Differ In Etiology, Pathology, Genetics, Age Of Onset, And Treatment.
Nephrogenic Diabetic Insipidus - Inherited Or Acquired Diabetes Insipidus Caused By Failure Of The Renal Tubules To Reabsorb Water In Response To Anti-Diuretic Hormone, Without Disturbance In The Renal Filtration And Solute Excretion Rates.
Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus ( NIDD, NIDDM ) - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Preclinical Diabetes - Former Name For Impaired Glucose Tolerance.
Renal Diabetes - Renal Glycosuria - That Due To Inherited Inability Of The Renal Tubules To Reabsorb Glucose Completely.
Subclinical Diabetes - Former Name For Impaired Glucose Tolerance.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus - One Of The Two Major Types Of Diabetes Mellitus, Characterized By Abrupt Onset Of Symptoms ( Often In Early Adolescence ), Insulinopenia, And Dependence On Exogenous Insulin; It Is Due To Lack Of Insulin Production By The Pancreatic Beta Cells, With Inadequate Control, Hyperglycemia, Protein Wasting, And Ketone Body Production Occur; The Hyperglycemia Leads To Overflow Glycosuria, Osmotic Diuresis, Hyperosmolarity, Dehydration, And Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Which Can Progress To Nausea & Vomiting, Stupor, And Potentially Fatal Hyperosmolar Coma. The Associated Angiopathy Of Blood Vessels ( Particularly Microangiopathy ) Affects The Retinas, Kidneys, And Arteriolar Basement Membranes. Polyuria, Polydipsia, Polyphagia, Weight Loss, Paresthesias, Blurred Vision, And Irritability Also Occur.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - One Of The Two Major Types Of Diabetes Mellitus, Peaking In Onset Between 50 And 60 Years Of Age, Characterized By Gradual Onset With Few Symptoms Of Metabolic Disturbance ( Glycosuria And Its Consequences ) And Control By Diet, With Or Without Oral Hypoglycemics But Without Exogenous Insulin Required. Basal Insulin Secretion Is Maintained At Normal Or Reduced Levels, But Insulin Release In Response To A Glucose Load Is Delayed Or Reduced. Defective Glucose Receptors On The Pancreatic Beta Cells May Be Involved. It Is Often Accompanied By Disease Of Blood Vessels, Particularly The Large Ones, Leading To Premature Atherosclerosis With Myocardial Infarction Or Stroke Syndrome.
Pathological Point Of View -
Universal Blue Circle Symbol For Diabetes ==>
1. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Also Known As Simply Diabetes, Is A Group Of Metabolic Diseases In Which There Are High Blood Sugar Levels Over A Prolonged Period.
- This High Blood Sugar Produces The Symptoms Of Frequent Urination, Increased Thirst, And Increased Hunger.
- Untreated, Diabetes Can Cause Many Complications.
- Acute Complications Include Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Nonketotic Hyperosmolar Coma.
- Serious Long-Term Complications Include Heart Disease, Stroke, Kidney Failure, Foot Ulcers And Damage To The Eyes.
Diabetes Is Due To Either The Pancreas Not Producing Enough Insulin, Or The Cells Of The Body Not Responding Properly To The Insulin Produced.
There Are Three Main Types Of Diabetes Mellitus:
- Type 1 DM Results From The Body's Failure To Produce Enough Insulin. This Form Was Previously Referred To As " Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus " (IDDM) Or " Juvenile Diabetes ". The Cause Is Unknown.
- Type 2 DM Begins With Insulin Resistance, A Condition In Which Cells Fail To Respond To Insulin Properly. As The Disease Progresses A Lack Of Insulin May Also Develop. This Form Was Previously Referred To As " Non Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus " (NIDDM) Or " Adult-Onset Diabetes ". The Primary Cause Is Excessive Body Weight And Not Enough Exercise.
- Gestational diabetes, Is The Third Main Form And Occurs When Pregnant Women Without A Previous History Of Diabetes Develop A High Blood Glucose Level.
Comparison of type 1 and 2 diabetes Feature Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Onset Sudden Gradual Age at onset Mostly in children Mostly in adults Body size Thin or normal[23] Often obese Ketoacidosis Common Rare Autoantibodies Usually present Absent Endogenous insulin Low or absent Normal, decreased
or increasedConcordance
in identical twins50% 90% Prevalence ~10% ~90%
2. Diabetes Insipidus (DI) Is A Condition Characterized By Excessive Thirst And Excretion Of Large Amounts Of Severely Diluted Urine, With Reduction Of Fluid Intake Having No Effect On The Concentration Of The Urine.
- There Are Different Types Of DI, Each With A Different Set Of Causes.
- The Most Common Type In Humans Is The Neurological Form, Called Central DI (CDI), Which Involves A Deficiency Of Arginine Vasopressin (AVP), Also Known As Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH). The Second Common Type Of DI Is Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (NDI), Which Is Due To Kidney Or Nephron Dysfunction Caused By An Insensitivity Of The Kidneys Or Nephrons To ADH. DI Can Also Be Gestational, Or Present As An Iatrogenic Artifact Of Alcohol Or Some Types Of Drug Abuse.
- DI Should Not Be Confused With Nocturia.
Signs & Symptoms :-
1. Diabetes Mellitus -
2. Diabetes Insipidus -
Difference B/w Diabetes Mellitus & Diabetes Insipidus :-
Pathophysiology :-
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus -
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus -
Gestational Diabetes -
Diabetes Insipidus -
For More Details :-
Management :-
Diagnosis :-
| Condition | 2 hour glucose | Fasting glucose | HbA1c |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | mmol/l(mg/dl) | mmol/l(mg/dl) | % |
| Normal | <7.8 (<140) | <6.1 (<110) | <6.0 |
| Impaired fasting glycaemia | <7.8 (<140) | ≥ 6.1(≥110) & <7.0(<126) | 6.0–6.4 |
| Impaired glucose tolerance | ≥7.8 (≥140) | <7.0 (<126) | 6.0–6.4 |
| Diabetes mellitus | ≥11.1 (≥200) | ≥7.0 (≥126) | ≥6.5 |
Allopathic Treatment :-
1. Diabetes Mellitus -
2. Diabetes Insipidus -
- Fluid Replacement Therapy.
- Desmopressin And Other Drugs.
" One Single Simple Drug Substance In Its Most Suitable Potency, According To Symptom Similarity Based On Totality! "
In Case Of Diabetes, List Of Useful Remedies (According To REPERTORY
DIABETES INSIPIDUS
Copious, profuse; polyuria; diuresis (See Diabetes.) -- Acet. ac., Acon., Alfal, Am. acet., Apoc., Arg. m., Arg. mur., Aur. mur., Ars., Bell., Bry., Cahinca, Can. ind., Caust., Cepa, Chin. s., Chionanth., Cina, Cod., Conv., Dulc., Equis., Eup. purp., Ferr. mur., Ferr. n., Gels., Glycerin, Glon., Gnaph., Guaco, Helleb., Helon., Ign., Indol, Kali c., Kali iod., Kali n., Kreos., Lact. ac., Led., Lil. t.,Lith. c., Lyc., Mag. p., Merc. c., Mosch., Murex, Nat. m., Niccol. s., Nit. ac., Nux. v., Ol. an., Oxytr., Phos. ac., Phos., Physal., Picr. ac., Plat. m. n., Puls., Quass., Rhus ar., Samb., Sang., Santon., Sars., Scilla, Sinap. n., Spart., Staph., Stroph., Sul., Tarax., Tereb., Thymol, Thyr., Uran., Verbasc., Verv. v.
Copious at night -- Ambra, Kali iod., Lyc., Murex, Petrol., Phos. ac., Quass., Scilla.
Copious at night -- Ambra, Kali iod., Lyc., Murex, Petrol., Phos. ac., Quass., Scilla.
DIABETES, Sugar -- Acet. ac., Adren., Am. acet., Arg. m., Arg. n., Aristol., Arn., Ars. br., Ars. iod., Ars., Asclep. vinc., Aur., Aur. mur., Bell., Bor. ac., Bov., Bry., Caps., Carb. ac., Ceanoth., Cham., Chel., Chimaph., Chionanth., Coca., Cod., Colch., Crot., Cupr. ars.,Cur., Eup. purp., Fel tauri, Ferr. iod., Ferr. mur., Fluor. ac., Glon., Glycerin, Grind., Helleb., Helon., Iod., Iris, Kali acet., Kali br., Kreos., Lach., Lact. ac., Lecith., Lycop., Lyc., Lyssin, Morph., Mosch., Murex, Nat. m., Nat. s., Nit. ac., Nux v., Op., Pancreat., Phaseol., Phos. ac., Phos., Phlorid., Picr. ac., Plumb. iod., Plumb., Pod., Rhus ar., Scilla, Sec., Sil., Sizyg., Strych. ars., Sul., Tar. h., Tarax., Tereb., Uran. n., Urea, Vanad.
Assimilative disorders -- Uran n.
Gastrohepatic origin -- Ars. iod., Ars., Bry., Calc. c., Cham., Chel., Kreos., Lact. ac., Lept., Lyc., Nux v., Uran n.Nervous origin -- Ars., Aur. mur., Calc. c., Ign., Phos. ac., Strych. ars.
Pancreatic origin -- Iris., Pancreat., Phos.
Concomitant
Gastrohepatic origin -- Ars. iod., Ars., Bry., Calc. c., Cham., Chel., Kreos., Lact. ac., Lept., Lyc., Nux v., Uran n.Nervous origin -- Ars., Aur. mur., Calc. c., Ign., Phos. ac., Strych. ars.
Pancreatic origin -- Iris., Pancreat., Phos.
Concomitant
Debility [with] -- Acet. ac., Op.
Gangrene, boils, carbuncles, diarrhœa [with] -- Ars.
Gouty symptoms [with] -- Lact. ac., Nat. s.Impotency [with] -- Coca, Mosch.
Melancholia, emaciation, thirst, restlessness [with] -- Helon.
Motor paralysis [with] -- Cur.
Rapid course [with] -- Cur., Morph.
Ulceration [with] -- Sizyg.
Gangrene, boils, carbuncles, diarrhœa [with] -- Ars.
Gouty symptoms [with] -- Lact. ac., Nat. s.Impotency [with] -- Coca, Mosch.
Melancholia, emaciation, thirst, restlessness [with] -- Helon.
Motor paralysis [with] -- Cur.
Rapid course [with] -- Cur., Morph.
Ulceration [with] -- Sizyg.
Our Next Topic Is "Myocardial Infarction".
I Need Your Help For More Precise Work........You Can Submit Your Work At ktthebest4u@gmail.com ; Last Day Of Submission Will Be Saturday, 06/8/2014.
Take Care Of Your Body,
It's The Only Place You Have To Live In.
With Best Regards, Karnav Thakkar :) :)


No comments:
Post a Comment